Hydrogeologist & Water Resources Specialist
Optimised for Desktop Viewing
This is the website of J. Malcolm Ashworth a freelance Hydrogeologist and Water Resources Specialist with +40 years of experience in ground and surface water data analysis, mapping, modelling, assessment and integrated water resource management. I offer independent and international expertise in quantifying and solving water resource and groundwater issues.Guiding principals:
1. Strive for excellence.
2. Put the client's interests first.
3. Tell the truth even if this challenges the client's opinion.
4. Only do work that I can do well.
5. Only advise work that is required to achieve mission results.
What I can offer you:
The following are some of the skills and services that I can offer you:
|
WATER RESOURCES
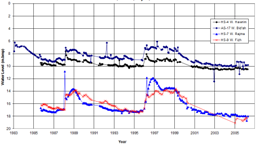
River Basin Assessment and Management: Social, economic, legal and political considerations aside, water resource management plans start with a comprehensive assessment of the components of a river basin’s water balance, available resources and the appreciation of how changes to one or more components of this balance affect other components and the environment in terms of quantity, quality and location. Information collated into databases and presented on maps, using ArcGIS, are key to a regional perspective for the management of water resource components. In general, four general categories of data are required.
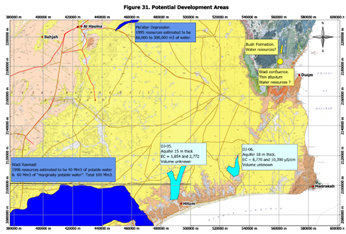
Expert services can be provided to collate and process water resources information from stakeholders, field inventories, pilot projects and the internet, onto ArcGIS maps, for assessment, management, reporting and presentation purposes. Exploration: Key sets of data required for groundwater resource assessments are often missing or inadequate. Drilling exploration boreholes, conducting aquifer tests, and initiating appropriate monitoring programs are then needed. Associated services that can be provided include facilitating remote sensing investigations (airborne, satellite and geophysical investigations), borehole designs, preparation of tender documents and specifications, supervision of drilling and borehole construction, aquifer and borehole testing, and analyses of data. Development: Effective groundwater management may require a range of different development options. The three most common requirements are:
Consulting services can be provided for the design, tendering, supervision (testing and construction) and management of these groundwater development options, or other schemes as required. Evaluations: Technical advice can be provided to determine the effectiveness of groundwater assessment, management and development programs. Conflict Solution: Technical advice can be provided to help resolve water conflicts |
|
||||||||||||
|
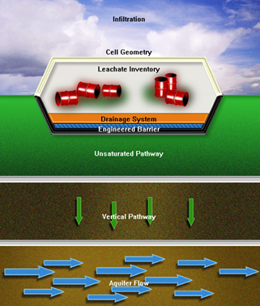
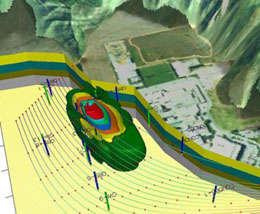
GROUNDWATER MODELLING Groundwater models are useful tools for solving and predicting groundwater flow and transport problems in aquifers. Typically these problems might involve: calculating the radius of influence of a well or wellfield; modelling the movement of leachate, leachate production, transportation and attenuation; and, calculating the impact of large scale groundwater abstractions on other users and on available resources. Analytical or numerical models can be deployed for solving these issues. The selection of the most appropriate model depends on the complexity of the problem at hand. Analytic Models Analytic models such as LANDSIM, CONSIM, GFLOW or BLUEBIRD, allow steady-state 2-D groundwater flow systems to be simulated using analytic functions. In these programs, a library of specialized “analytic elements” are superimposed to model a variety of features such as head of leachate, flow rates, engineered barriers, advective transport, contaminant concentration, drains, slurry walls, wells and reservoirs. The functions associated with these elements meet Darcy’s law and Mass Continuity equations everywhere in the domain. Some of these models such as LANDSIM and CONSIM are specially designed to produce estimates of possible contaminant concentrations using probabilistic assessment techniques. Numerical Models
Numerical models such as the U.S. Geological Survey’s (USGS) developed Modular
Finite-Difference Flow Model (MODFLOW) provide the code for solving groundwater
flow and contaminant transport in 3-D. Since its development in 1983, numerous
codes or packages have been developed for MODFLOW. Packages can be stand-alone
codes or can be integrated with MODFLOW. These packages include advective
transport model (PMPATH), the solute transport model (MT3D), parameter
estimation programs (PEST), solute transport model (MOC3D), inverse models (MODFLOWP)
and seawater intrusion (SEAWAT). Commercial software, such as the Groundwater Modelling System (GMS), can be deployed that integrates these packages with analysis and calibration tools and 3D visualization capabilities into a single software environment. |
|
||||||||||||
|
ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENT &
COMPLIANCE WITH REMEDIAL TARGETS
Expert services can be provided to assist with Environmental Assessments and Remediation, including: Field Investigations, Laboratory Analyses and Monitoring: Sampling to identify and delimitate sources of contamination, field investigations to characterise the extent of soil and groundwater contamination, laboratory tests to determine the properties of the soil, aquifer and contaminant, and monitoring to ensure contaminants concentrations meet acceptable levels. Soil and Groundwater Risk Assessments: Risk analyses of soil and groundwater vulnerability using a variety of techniques (UK Level 1 to 4 procedures, numerical and analytic groundwater models, or ArcGIS overlay and index methods) to ensure compliance with Environment Agency standards. |
|||||||||||||
Countries of work-experience.